Comparing DASH and Mediterranean diets: benefits, differences and ideal fit

Lead Dietitian for the Mayo Clinic Diet
In a world full of trendy diets and quick-fix plans, two eating patterns have earned the trust of health professionals and everyday eaters alike: the Mediterranean Diet and the DASH diet. These science-backed approaches emphasize whole foods, heart health, and sustainable habits, making them long-standing favorites among people seeking to lose weight, lower blood pressure, or simply feel better day to day.
If you’re wondering which plan is right for you, you’re not alone. Both the Mediterranean Diet vs. DASH debate centers around improving overall well-being, and each has distinct strengths. This guide will walk you through their core differences, health benefits, and how to choose the best fit for your lifestyle and goals.
Overview of the Mediterranean diet
The Mediterranean lifestyle diet is inspired by the traditional eating habits of people in countries bordering the Mediterranean Sea, including Greece, Italy, and Spain. Rather than a strict set of rules, it’s a flexible approach that encourages fresh, flavorful meals rooted in plant-based nutrition.
Core foods include:
- Fruits and vegetables
- Whole grains
- Legumes and nuts
- Olive oil as the primary fat
- Moderate amounts of fish and poultry
This diet also promotes social eating and regular physical activity, adding a cultural and lifestyle component that many find easier to maintain.
Health outcomes:
The Mediterranean diet has been linked to:
- Reduced risk of heart disease and stroke
- Lower LDL (“bad”) cholesterol levels
- Improved cognitive health
- Lower incidence of type 2 diabetes
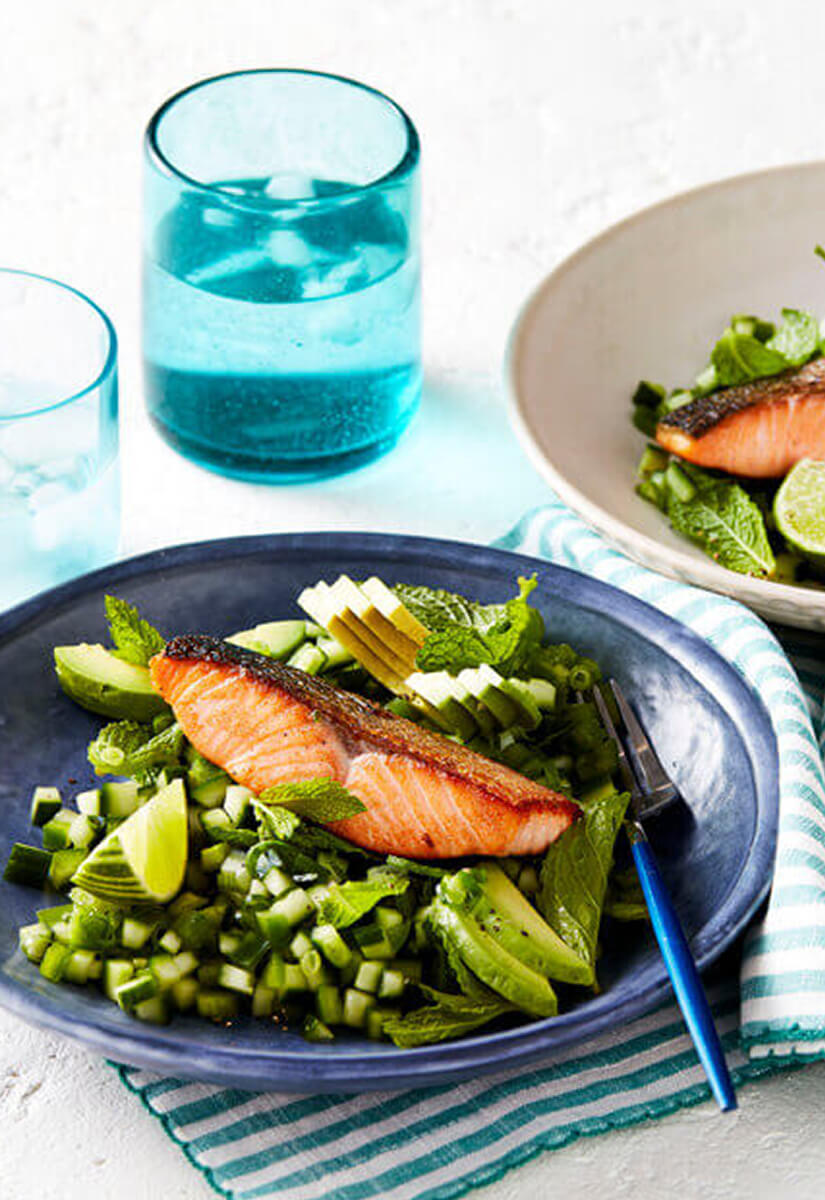
The Mediterranean features fish and healthy fats in addition to fruits, vegetables and legumes
The Mayo Clinic Diet’s Mediterranean meal plan follows these principles while offering structure for weight loss. It blends flexibility with expert-approved guidelines for portion sizes, meal prep, and nutritional balance—helping members adopt this healthy pattern for the long haul.
This plan is also featured in the Mayo Clinic Diet for Heart Health, a 24-week program designed for people managing high blood pressure, high cholesterol, or heart disease. The program combines diet, exercise, sleep, and stress management to help naturally reduce blood pressure and improve heart health.
Overview of the DASH diet
The DASH diet, short for Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension, was developed by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute to help individuals manage or prevent high blood pressure.
Its key focus: limiting sodium intake while boosting nutrients that support healthy blood pressure particularly potassium, calcium, and magnesium.
Core foods include:
- Vegetables and fruits
- Whole grains
- Low-fat dairy
- Lean protein sources (especially poultry and fish)
- Nuts, seeds, and legumes
Foods to limit:
- High-sodium processed items
- Added sugars
- Red meats
- Saturated fats
Numerous studies—including those supported by the National Institutes of Health—have shown that the DASH diet can:
- Lower systolic and diastolic blood pressure
- Support healthy weight loss
- Improve heart health markers (e.g., cholesterol, triglycerides)
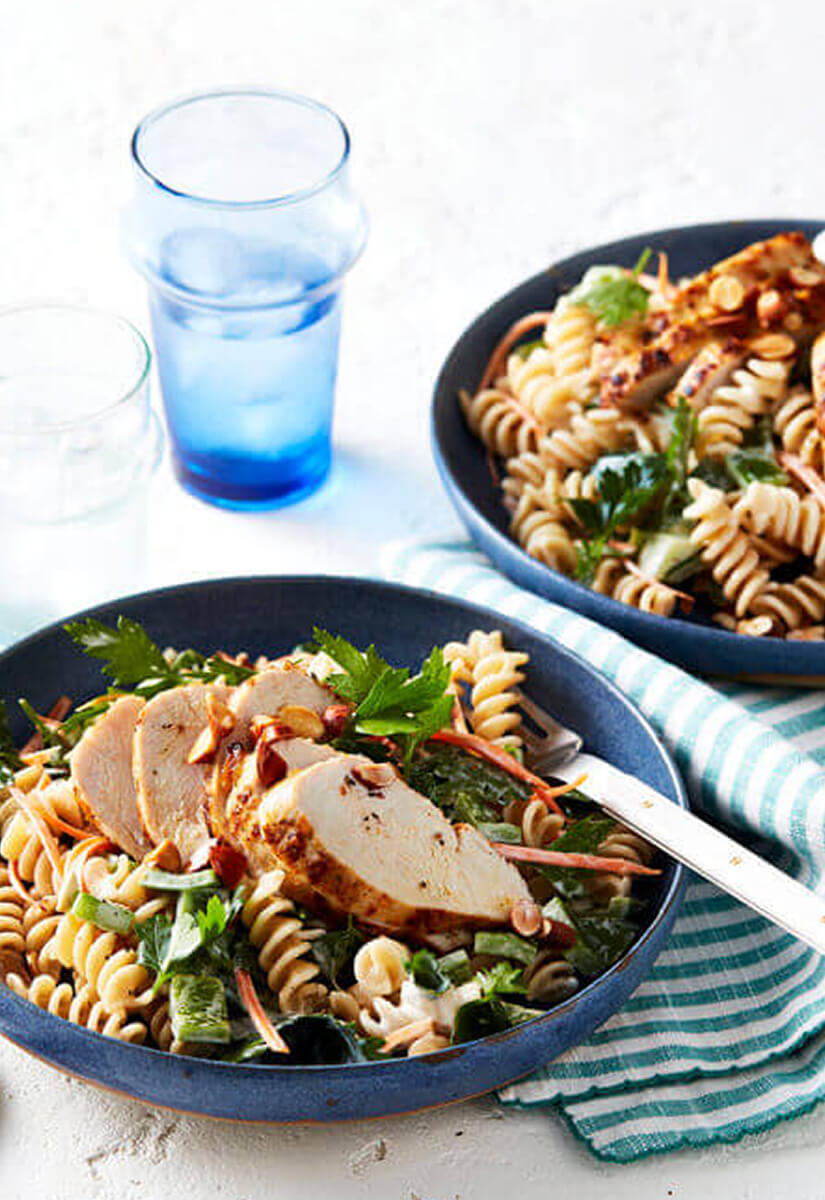

The DASH diet features lean protein and low-fat dairy in addition to fruits, vegetables and whole grains
Endorsed by the American Heart Association, the DASH diet is often recommended for people with prehypertension or a family history of heart disease.
The Mayo Clinic Diet’s Original meal plan is closely aligned with DASH principles. It emphasizes whole foods, low sodium intake, and balanced meals—making it a great entry point for individuals seeking a practical, science-based approach to eating.
Both the Mediterranean and Original DASH-style meal plans are also part of the Mayo Clinic Diet for Heart Health program. This targeted program supports people looking to lose weight and take control of their cardiovascular health with proven tools, education, and heart-friendly meal options that are both DASH and Mediterranean aligned.
Side-by-side comparison chart: DASH vs. Mediterranean
Below is a quick reference comparing the two diets:
| Feature | Mediterranean diet | DASH diet |
| Primary goal | Overall wellness, heart and brain health | Lower blood pressure, heart health |
| Core foods | Vegetables, fruits, whole grains, legumes, fish, olive oil | Vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean meats, low-fat dairy |
| Fat sources | Healthy fats (esp. olive oil, nuts) | Limited fats; low in saturated fat |
| Sodium intake | Moderate (not overly restricted) | Low sodium (often <2,300 mg/day) |
| Red meat | Limited | Limited |
| Dairy | Moderate (mostly yogurt, cheese) | Emphasized (low-fat) |
| Wine | Optional, in moderation, but not endorsed | Not typically included |
| Lifestyle emphasis | Strong (social meals, activity) | Some (exercise encouraged) |
| Scientific backing | Yes, especially for heart/cognitive health | Yes, especially for blood pressure control |
Video: Dr. Lopez offers advice on starting a heart healthy diet
Which diet is best for…?
Heart health: Both diets shine here. The Mediterranean diet supports heart health through high levels of monounsaturated fats (like olive oil) and omega-3s from fish. The DASH diet lowers blood pressure by limiting sodium and emphasizing potassium-rich foods.
Weight loss: Neither is designed as a “weight-loss diet,” but both support healthy, gradual weight reduction when paired with lifestyle changes and calorie reduction. The Mayo Clinic Diet’s versions of both plans add structured calorie control and meal guidance, helping people reach their goals sustainably.
Long-term sustainability: The Mediterranean diet often feels less restrictive. It allows for flavorful fats, diverse cuisines, and social enjoyment. DASH can be equally sustainable, though sodium restrictions may take adjustment.
Diabetics or pre-diabetics: Both diets help regulate blood sugar. Mediterranean patterns can improve insulin sensitivity. DASH limits added sugars and processed carbs. Choosing whole, fiber-rich foods is key in both.
Individuals with high blood pressure: The DASH diet is specifically designed to reduce blood pressure and has decades of supporting data. It’s often a first recommendation for people managing hypertension.
Pros and cons of each diet
| Mediterranean diet pros: | Mediterranean diet cons: |
|
|
| DASH diet pros: | DASH diet cons: |
|
|
Accessibility and cost: Both diets prioritize whole foods, which may cost more upfront but reduce reliance on packaged products. The Mayo Clinic Diet meal plans help members with shopping lists, meal prep guidance, and recipes tailored to either dietary style.
How to choose the right plan for your goals
Start by asking yourself:
- Do I need to manage high blood pressure?
- Am I looking for a flexible plan?
- Do I need stricter structure or prefer intuitive eating?
Choose Mediterranean if you:
- Love variety and rich flavors
- Want a more lifestyle-based approach
- Are looking to support cognitive and heart health long-term
Choose DASH if you:
- Need to control blood pressure quickly
- Are sensitive to salt or have family history of hypertension
Both are great options for overall health. And with the Mayo Clinic Diet, you can align with either approach while getting the tools to stay on track—meal plans, trackers, personalized support, and more.
5 expert tips for success on either diet
- Start small. Swap butter for olive oil. Add one more serving of veggies a day. Gradual changes stick better than big overhauls.
- Shop smart. Use a grocery list to stock up on staples like whole grains, canned beans, frozen vegetables, and lean proteins.
- Prep ahead. Pre-chop veggies, cook batches of brown rice or quinoa, and portion out nuts or snacks to stay on track.
- Don’t skip flavor. Herbs, spices, citrus, and vinegars add depth without extra salt or fat.
- Make it social. Invite friends to share a Mediterranean-style meal or walk after dinner—both diets thrive on healthy habits, not isolation.
Which diet fits you best?
Both the Mediterranean diet vs. DASH offer proven, healthy ways to eat well for life. Rather than short-term fixes, these plans support long-term well-being—from heart health to blood pressure control and beyond.
Your choice may come down to lifestyle preferences, cultural food traditions, or specific health goals. Either way, both paths are grounded in real science—and made easier with the support of the Mayo Clinic Diet’s expert-backed meal plans.
If you’re still unsure, consider speaking with a registered dietitian or trying a week of each to see what feels right.
Related Posts
Explore Topics
Success Stories (34) Food & Nutrition (25) Exercise (3) Habits & Motivation (12) Weight-Loss Medications (16) Weight Loss (4)

Free weight loss calculator
Discover how long it will take to reach your weight loss goals with our free weight loss calculator.