Mediterranean diet and inflammation: Foods that soothe chronic pain
The role of diet in inflammation
Living with chronic pain—whether from arthritis, autoimmune flare-ups, or nagging back and knee discomfort—can feel like you’re carrying invisible weight every day. But for many, a combination of diet and healthy lifestyle habits can offer relief. One inspiring example: Victoria Hailey, who began the Mayo Clinic Diet in January 2023, lost 58 pounds, and by the end of the year, her persistent knee and back pain disappeared entirely, alongside normalized blood pressure and lab results.
Victoria says: “I felt like I was carrying an extra 80‑pound weight everywhere I went,” and that landing on a sustainable eating plan changed everything. Her journey shows the real connection between weight loss and reduced inflammation—and how the Mayo Clinic Diet’s structure helped her keep the change for good.
Recent studies support this link: even moderate weight loss can reduce inflammatory markers like C‑reactive protein (CRP) and ease chronic pain related to joint stress.
What causes inflammation?
Inflammation is your body’s natural defense mechanism against injury or infection. But when inflammation becomes chronic — persisting for weeks, months, or even years — it can damage healthy tissues and contribute to a wide range of conditions including arthritis, cardiovascular disease, autoimmune disorders, and even depression.
Common causes of chronic inflammation include:
- A diet high in processed or sugary foods
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Chronic stress
- Environmental toxins
- Excess weight
- Smoking or excessive alcohol use
The link between inflammation and disease
Chronic inflammation plays a central role in many long-term health issues, including:
- Rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis
- Type 2 diabetes
- Heart disease
- Obesity
- Certain cancers
- Alzheimer’s disease
Emerging studies even suggest that low-grade inflammation may contribute to accelerated aging.
What role does diet play in inflammation?
Certain foods can either fuel or fight inflammation. Diets high in added sugars, trans fats, and processed meats are known to promote inflammation. On the other hand, diets rich in fiber, antioxidants, omega-3s, and phytonutrients can help soothe it.
That’s where the anti-inflammatory Mediterranean diet shines.
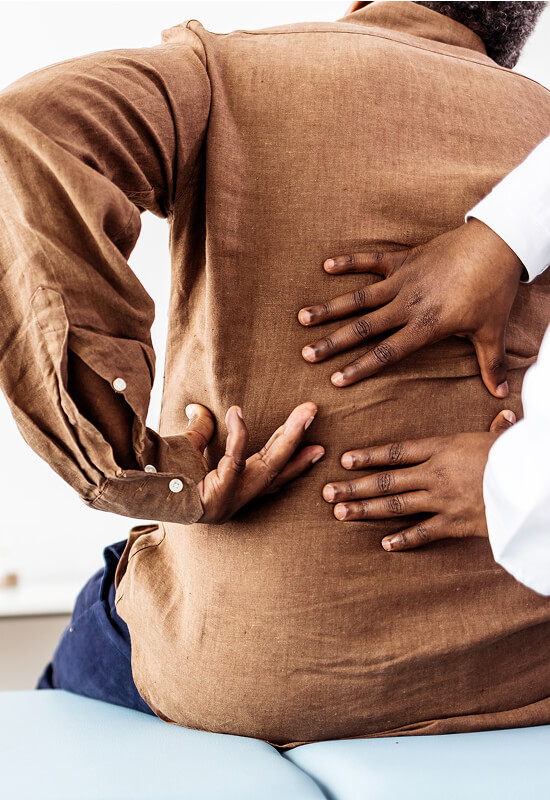
Chronic inflammation plays a role in many long-term health issues, such as rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis
How does the Mediterranean diet fight inflammation?
The mediterranean diet inflammation relationship is supported by decades of research. Here’s how this eating pattern can soothe pain and support overall wellness:
|
Mediterranean diet features |
How they help inflammation |
|
Rich in antioxidants and polyphenols |
Bright produce, legumes, herbs, and whole grains deliver polyphenols that help neutralize inflammation-causing free radicals. |
|
Healthy fats reduce inflammatory markers |
Olive oil—especially extra-virgin—contains oleocanthal, which has anti-inflammatory properties. Paired with nuts, seeds, and omega-3-rich fish, these fats help lower CRP and ease inflammation naturally. |
|
Whole-food focus with minimal processing |
The Mayo Clinic Diet Mediterranean meal plan and the Heart Smart Superfoods meal plan are built around whole foods with minimal added sugars or ultra-processed items—creating a naturally anti-inflammatory foundation. |
|
Gut health support through fiber |
High-fiber foods from the Mediterranean diet nourish beneficial gut bacteria, helping balance the microbiome and reduce systemic inflammation. |
Victoria’s story: how weight loss and the Mayo Clinic Diet eased chronic pain
Victoria Hailey’s experience is a powerful testament to how weight loss combined with anti-inflammatory eating can restore health. Victoria struggled with chronic knee and back pain, lab results out of range, and difficulty climbing stairs—until she found the Mayo Clinic Diet program. By September 2023, she had lost 58 pounds, her lab work normalized, and her blood pressure came under control. Best of all, her knee and back pain were gone—she could run up stairs for the first time in years.
What made the difference for her?
- The meal plans (especially Mediterranean-style recipes) made portion control and healthy choices effortless.
- The Mayo Clinic Diet app helped Victoria track food, progress, and stay on task with grocery lists and recipes she could tailor.
- A supportive community—including the private Facebook group—kept her motivated, as did the science-backed structure of habits and tracking.
Her advice to others: “Trust the process. It works. The Mayo Clinic Diet is backed by science and provides all the tools you need to succeed.”
Victoria’s transformation shows that weight loss itself can reduce joint stress and inflammation, while whole‑food, anti‑inflammatory eating supports healing from the inside out.
What are the best anti-inflammatory foods?

Let’s dig into the top anti-inflammatory foods for autoimmune disease, joint pain, and overall inflammation relief—all featured in the Mediterranean diet.
Anti-inflammatory vegetables and greens
- Leafy greens (spinach, kale, Swiss chard)
- Cruciferous vegetables (broccoli, cauliflower, Brussels sprouts)
- Sweet potatoes and beets
- Onions, garlic, leeks
These veggies are rich in fiber, vitamins C and K, and flavonoids that actively reduce inflammation.
Heart-healthy fats and oils
- Extra virgin olive oil (rich in oleocanthal)
- Omega-3 rich fish (salmon, sardines, mackerel)
- Avocados
- Walnuts, flaxseeds, chia seeds
These fats help regulate the body’s inflammatory response and protect against heart disease.
Antioxidant-rich foods
- Berries (blueberries, strawberries, raspberries)
- Grapes and pomegranates
- Tomatoes
- Herbs like turmeric, oregano, rosemary, basil
These are among the most potent foods that fight chronic inflammation.
High-fiber whole plant foods
- Lentils and chickpeas
- Quinoa, farro, oats
- Apples, pears, oranges
- Nuts and seeds
Fiber helps reduce inflammation by supporting healthy gut bacteria and stabilizing blood sugar levels.
Explore these foods in action with the Mayo Clinic Diet’s Mediterranean meal plan or the Heart Smart Superfoods meal plan.
What foods trigger inflammation?

Knowing what to limit is just as important as knowing what to eat. Here are the biggest dietary culprits:
Refined sugars and refined carbohydrates
- Sugary beverages
- White bread and pastries
- Candy and desserts
These spike blood sugar and insulin, promoting systemic inflammation.
Processed and red meats
- Bacon, sausage, deli meats
- Conventional red meat in excess
These contain compounds like AGEs (advanced glycation end products) that trigger inflammatory responses.
Unhealthy fats and oils
- Trans fats (partially hydrogenated oils)
- Excess saturated fats (fried foods, fast food)
These fats can increase CRP levels and negatively affect heart health.
Ultra-processed and packaged foods
- Chips, crackers, frozen meals
- Packaged snacks with additives and preservatives
These foods are often nutrient-poor, high in sodium and refined carbs.
Alcohol and artificial additives
- Excess alcohol
- Artificial sweeteners, dyes, and emulsifiers
These can disrupt gut health and trigger inflammatory pathways.
Quick tips to reduce inflammation daily
- Begin each meal with plenty of vegetables
- Swap butter for extra‑virgin olive oil
- Choose fish or legumes instead of red meat
- Snack on fresh fruit, vegetables and nuts
- Skip sugary drinks; choose water or herbal teas
- Batch-cook anti-inflammatory Mediterranean meals
- Track meals and reach your goals with the Mayo Clinic Diet app
- Take the free quiz to get your Mayo Clinic Diet Score and breathe easier knowing your inflammation-fighting strategy is backed by science
Key takeaways
Victoria’s story illustrates that chronic inflammation and pain don’t have to be lifelong burdens. Through the anti-inflammatory Mediterranean diet, paired with safe, sustainable weight loss on the Mayo Clinic Diet, pain relief and renewed vitality are within reach. The Diet’s Mediterranean and Heart Smart Superfoods meal plans blend whole foods, healthy fats, fiber, and antioxidants—minimizing processed ingredients and added sugars.
If you’re ready to feel like yourself again, try the Mayo Clinic Diet, where meal plans, tools, support, and real-life success like Victoria’s guide your journey.
Frequently asked questions
Can food alone reduce inflammation?
Food plays a powerful role in managing inflammation, especially when paired with other healthy lifestyle habits. While food alone may not cure chronic conditions, a diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods—like the Mediterranean diet—can reduce flare-ups, ease joint pain, and support better overall health. A healthy diet can contribute to weight loss, which also reduces inflammation.
How fast does an anti-inflammatory diet work?
Some people notice reduced symptoms (like joint stiffness or bloating) within days or weeks of making changes. However, long-term benefits such as lower inflammatory markers or weight loss typically take 4–12 weeks or more, depending on individual factors and consistency.
What are the worst foods for inflammation?
Highly processed foods, added sugars, trans fats, red and processed meats, and excessive alcohol are top offenders. These trigger inflammatory pathways and worsen chronic pain symptoms over time. Replacing them with whole, unprocessed foods is one of the best steps you can take.
Related Posts
Explore Topics
Success Stories (34) Food & Nutrition (25) Exercise (3) Habits & Motivation (12) Weight-Loss Medications (16) Weight Loss (4)

Free weight loss calculator
Discover how long it will take to reach your weight loss goals with our free weight loss calculator.